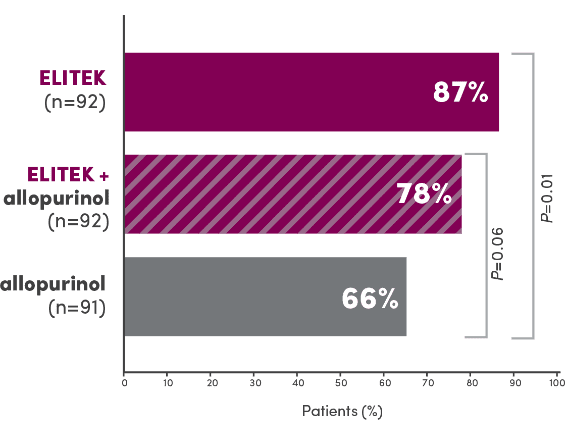
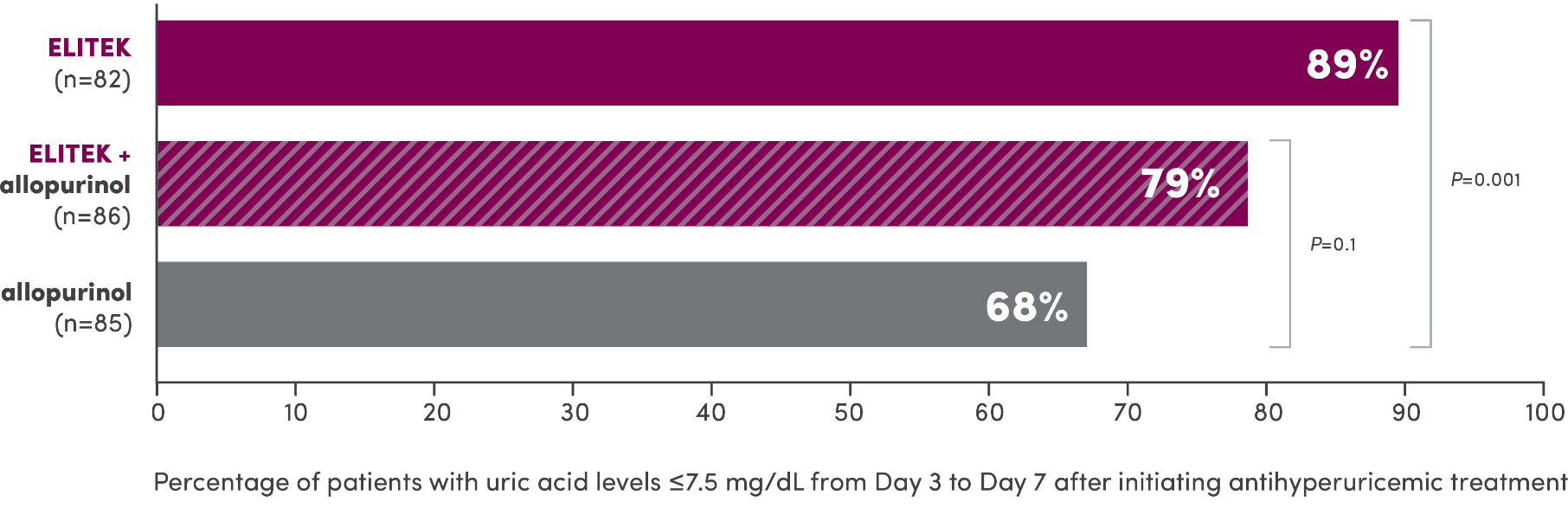
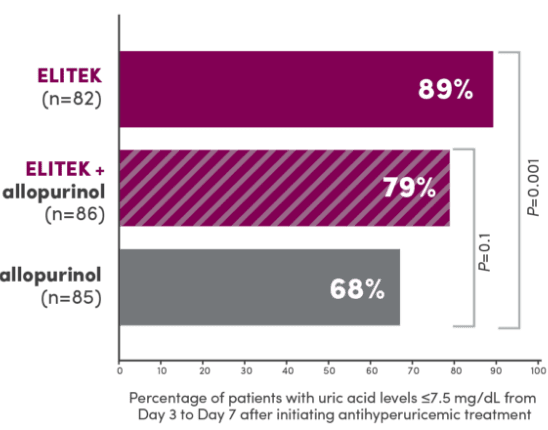
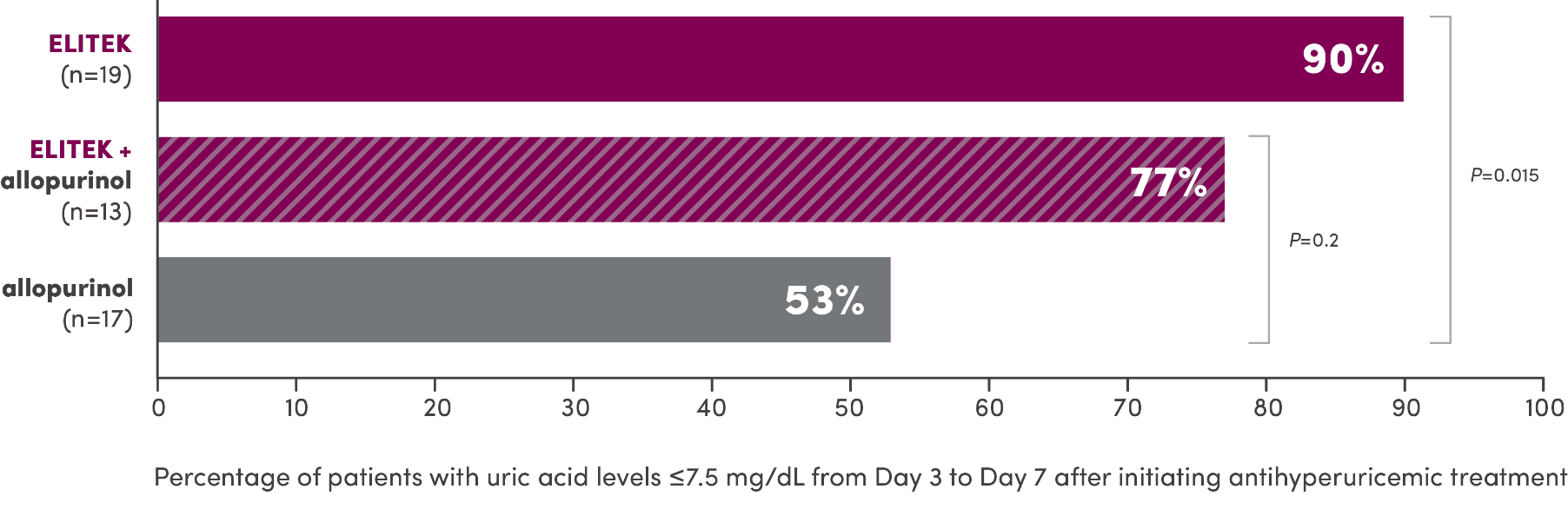
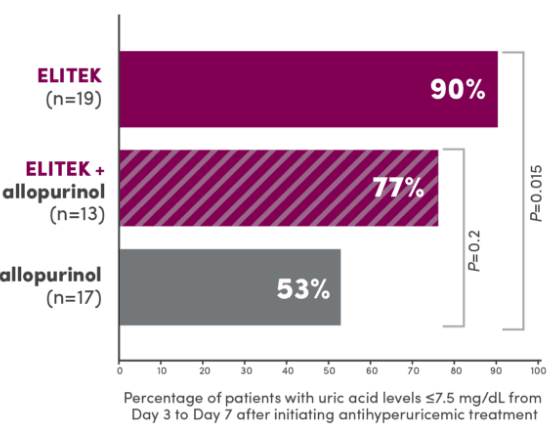
A head-to-head trial vs allopurinol demonstrated superior efficacy in maintaining normal uric acid levels1
Proportion of patients with normal uric acid levels ≤7.5 mg/dL from Day 3 to Day 7 after initiating antihyperuricemic treatment (primary endpoint)1
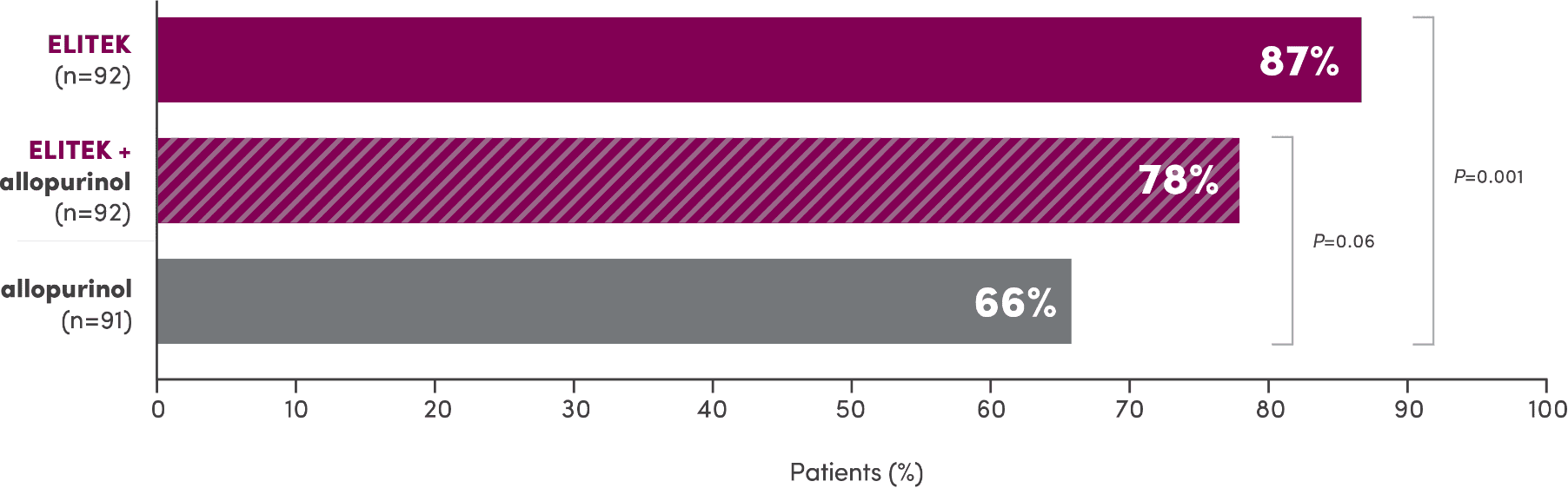
Unlike allopurinol, ELITEK maintained normal uric acid levels in 100% of assessable adult patients2
Documented failure rate in hyperuricemic and nonhyperuricemic adult patients2
- The ELITEK, ELITEK + allopurinol, and allopurinol arms had 13%, 15%, and 19% missing uric acid samples, respectively. The uric acid failure status in those patients is unknown2

No adult patients receiving ELITEK alone required antihyperuricemic treatment past 5 days2
See the full context of ELITEK efficacy and safety
Read the Clinician's Guide for an in-depth overview of ELITEK clinical data
DOWNLOAD NOW
CLL=chronic lymphocytic leukemia; DLBCL=diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; SLL=small lymphocytic lymphoma.
References: 1. Cortes J, Moore JO, Maziarz RT, et al. Control of plasma uric acid in adults at risk for tumor lysis syndrome: efficacy and safety of rasburicase alone and rasburicase followed by allopurinol compared with allopurinol alone—results of a multicenter phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(27):4207-4213. 2. ELITEK [prescribing information]. Bridgewater, NJ: sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC. 3. Data on file. Bridgewater, NJ: sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC. 4. Howard SC, Jones DP, Pui CH. The tumor lysis syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(19):1844-1854. 5. Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma. V.3.2022. ©National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2020. All rights reserved. Accessed August 26, 2022. To view the most recent and complete version of the guideline, go online to NCCN.org. NCCN makes no warranties of any kind whatsoever regarding their content, use or application and disclaims any responsibility for their application or use in any way.